Smart contracts are revolutionizing various industries by enabling secure, transparent, and efficient transactions. Initially popular in the cryptocurrency sector, their applications have expanded to include insurance, real estate, IoT, and more. Understanding what smart contracts are and how they work is crucial for leveraging their full potential.
In this blog, we delve into the fundamentals of smart contracts, their key advantages, and their future prospects.

What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are popular in the crypto industry, primarily for exchanging cryptocurrencies. Their use extends to insurance and real estate, offering better scalability at lower costs.
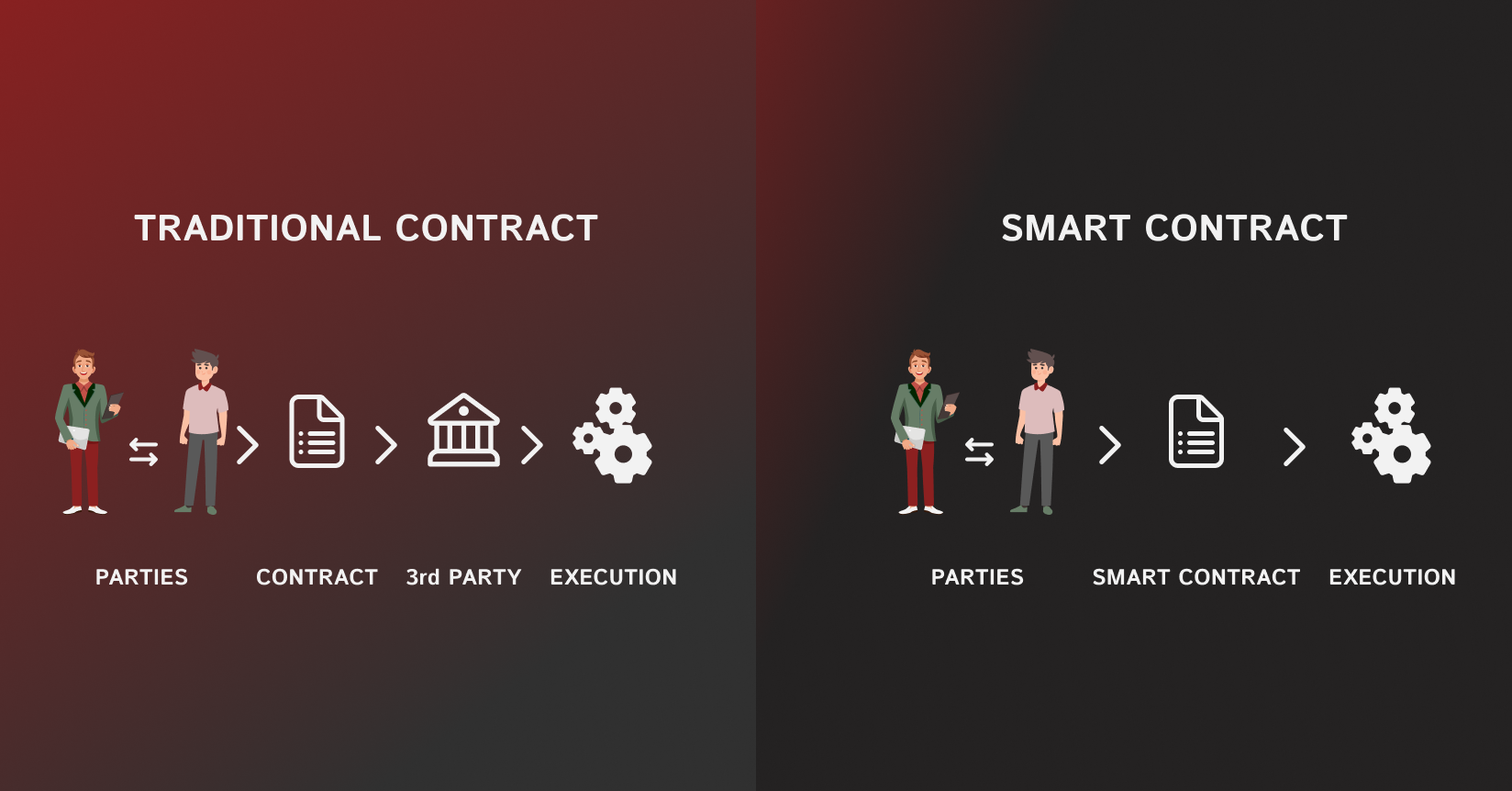
Automated and straightforward, smart contracts are created based on pre-defined conditions. Built on blockchain technology, they eliminate administrative overhead by relying on distributed ledgers for transaction confirmation. Written in code, smart contracts automatically transfer funds once the predefined requirements are met, facilitating transactions without intermediaries. This reduces payment delays, errors, and the complexity of traditional contracts, ensuring reliable and credible transactions.
Primary Purpose of Smart Contracts in the Blockchain
The primary purpose of smart contracts is to facilitate transactions by eliminating intermediaries like courts and arbitrators involved in traditional business processes. These automated contracts execute predefined conditions set in code, ensuring that transactions are reliable and efficient.
By removing intermediaries, smart contracts reduce payment delays, errors, and the complexity associated with conventional contracts while maintaining authenticity and credibility. This streamlined process allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions, making smart contracts a powerful tool for enhancing business operations on the blockchain.
How Did Smart Contracts Come to Life?
The concept of smart contracts predates blockchain technology and was first proposed by Nick Szabo, a prominent American cryptographer. In 1996, Szabo wrote an essay in Extropy magazine outlining the potential benefits and characteristics of smart contracts. Over the years, he expanded on these ideas in various publications, highlighting how automated, self-executing contracts could revolutionize business transactions.
In the same year, Ian Grigg and Gary Howland also contributed to the development of smart contract concepts through their research on Ricardian contracts within the Ricardo payment system.
The advent of Bitcoin and its blockchain technology provided the necessary foundation for implementing smart contracts. This technique saw its first practical application on the Ethereum blockchain, which introduced a robust platform for developing and executing smart contracts. Today, many other platforms support smart contracts, but Ethereum remains a pioneer and leader in this field.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
The mechanics of smart contracts can be likened to a vending machine. Just as a vending machine operates without the need for a human vendor, smart contract transactions eliminate the need for intermediaries. If the specified conditions are met, the transaction is automatically executed.
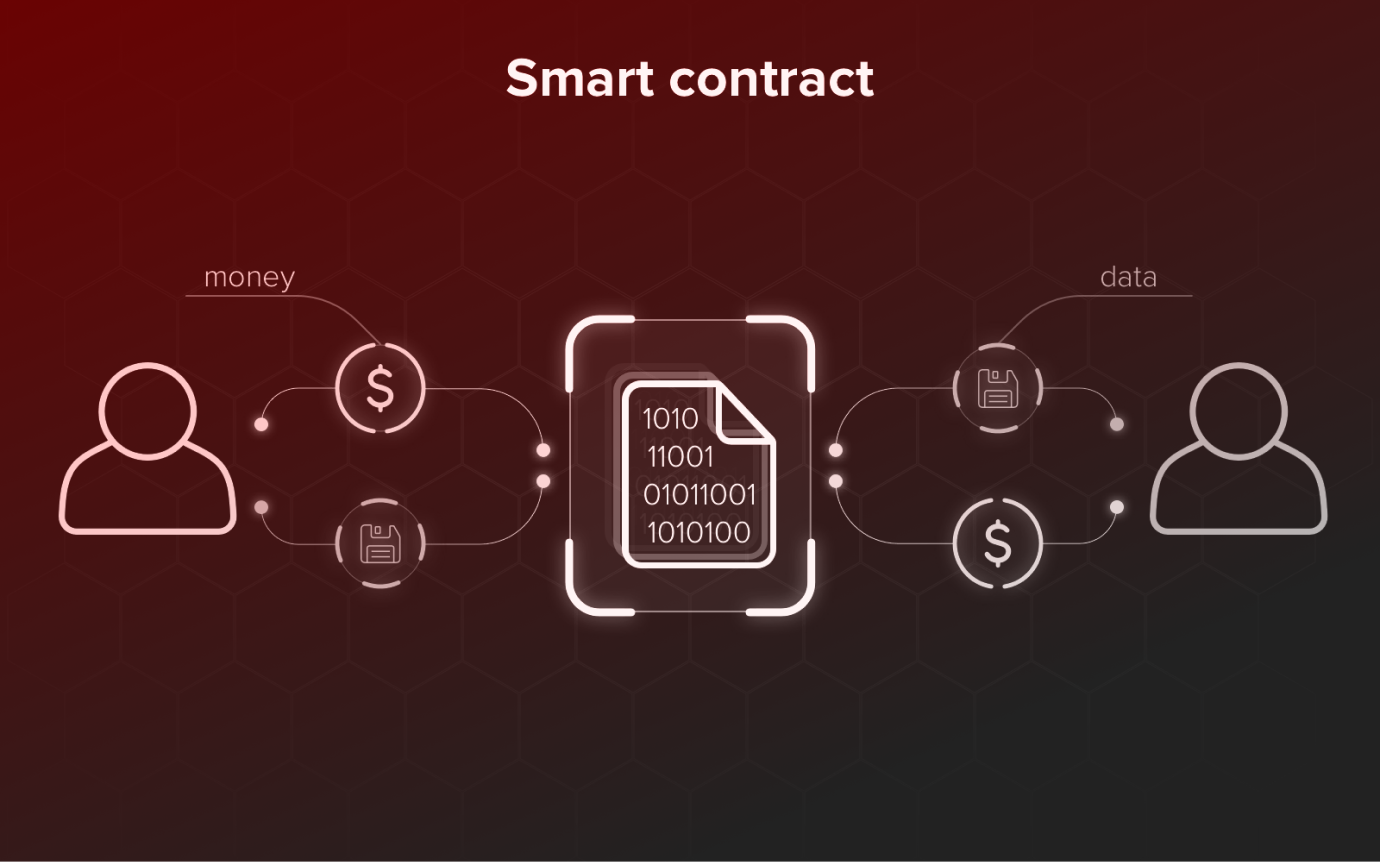
In technical terms, once a smart contract agreement is established between two parties, they agree on the conditions under which the contract will be considered complete. These conditions are then encoded into the smart contract, which is encrypted and stored on the blockchain network.
When the conditions of the contract are fulfilled, the smart contract automatically executes the transaction. This transaction is then recorded on the blockchain, and all nodes in the network update their copies of the blockchain to reflect the completed transaction.
In essence, smart contracts guarantee that when the right inputs are provided, the agreed-upon output is assured. They not only define the rules and penalties of an agreement but also automatically enforce the contractual obligations, ensuring reliability and trustworthiness without the need for intermediaries.
Smart Contracts Key Advantages
There are several benefits of Smart Contracs, including:
-
Independence: Smart contracts operate independently, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as brokers or lawyers. This independence reduces the risk of third-party manipulation and ensures objectivity by removing potential biases and errors associated with human intermediaries.
-
Transparency: All documents and transactions are encrypted and recorded in a common ledger shared by the involved parties, ensuring complete transparency. This means no one can claim loss or misplacement of information, as everything is securely documented and accessible.
-
Backup: Blockchain technology ensures that multiple copies of the documents are stored across the network, providing robust backup and protection against data loss.
-
Speed: Smart contracts automate tasks through software code, significantly reducing the time spent on manual processing. This automation ensures faster execution of agreements and transactions.
-
Savings: The elimination of intermediaries leads to substantial cost savings. Without the need to hire legal representatives or other third parties, transactions become more economical.
-
Precision: Automation in smart contracts minimizes errors. The precision of automated processes reduces the chances of mistakes that are common in manual form filling, further enhancing cost efficiency and speed.
-
Safety: The encryption of blockchain transactions makes smart contracts highly secure and difficult to hack or alter. Since each record is linked to the previous one, altering a single record would require changing the entire chain, making unauthorized modifications extremely challenging.
While smart contracts are secure, they are not immune to human errors during coding. It is crucial to avoid coding mistakes that could expose the contract to hacking. Smart contracts are also not reversible. Therefore, it is essential to ensure accuracy and correctness before placing them on the blockchain. Once deployed, correcting or altering a smart contract can be complex and costly.
Smart Contracts Key Elements
A smart contract comprises several key elements that ensure its proper function and enforceability:
-
Signatures: All involved parties must digitally sign the contract, indicating their agreement to the stipulated conditions. This is crucial for finalizing the deal and making it legally binding.
-
Contract's Subject Matter: The object or subject of the contract must be clearly defined and included within the smart contract. This ensures that all parties are aware of what is being agreed upon and what the contract pertains to.
-
Specific Terminology: Terms and conditions within the smart contract should be precisely defined and thoroughly detailed. For instance, Ethereum smart contracts use programming languages like Solidity and Serpent, so the agreement must adhere to specific mathematical and logical concepts consistent with these languages to ensure accuracy and enforceability.
Examples of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are not only pivotal for trading cryptocurrencies but also have versatile applications across various industries such as financial services, IoT, logistics, and more.
Smart contracts enable secure, distributed access control to IoT systems. This means that everyday household items with internet capabilities can be managed more efficiently and securely through smart contracts, enhancing automation and connectivity in smart homes.
In human resources, smart contracts simplify the management of employee data, including salaries, competencies, and responsibilities. These contracts ensure transparency and trust between employers and employees by recording all pertinent information in an immutable and transparent manner.
- Logistics and Supply Chain
Traditional supply chains often face bureaucratic delays and are prone to fraud and loss. Smart contracts streamline these processes by providing a secure, digital, and accessible record for all parties involved. This automation reduces delays and enhances the efficiency of supply chain management.
Managing and verifying the ownership of content can be challenging, especially when multiple parties are involved. Smart contracts simplify this process by clearly defining and enforcing the rights and obligations of each party involved in the creation and distribution of copyrighted content.
The rise of cryptocurrencies has led to numerous financial applications utilizing smart contracts. These include systems that conduct auctions, automatically verify and reimburse bids, and manage decentralized lotteries. Smart contracts in the financial sector enhance security, efficiency, and trust.
Blockchain Platforms for Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are supported by various blockchain platforms, each with unique features and capabilities:
-
**Bitcoin:** While the Bitcoin blockchain supports basic smart contracts, it is primarily designed for value transfers and lacks the flexibility for more complex contracts.
-
**NXT:** Offers templates for smart contracts but has limited customization options.
-
**Ethereum:** Known for its advanced coding capabilities and flexibility, Ethereum supports complex smart contracts. However, it can be costly as users need to pay ETH tokens for computing power.
-
**Stellar:** Provides a user-friendly interface and superior speed and security compared to Ethereum. It is best suited for executing simpler smart contracts.
-
**Cardano:** A smart contract platform focused on security through a layered design. It is the first blockchain initiative based on peer-reviewed academic research and scientific philosophy.
Popular applications of smart contracts include online financial platforms like MakerDAO and Compound, and decentralized exchanges like Uniswap.
The Future of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are set to play an increasingly significant role in various industries. While they may not completely replace traditional contracts, their usage will certainly reduce reliance on conventional methods, especially for transactions involving goods, services, and rights. The adoption of smart contracts will likely expand into new areas of daily life.
In the coming years, many countries will address the legal challenges associated with smart contracts. This shift is already underway, with states like Arizona and Nevada updating their versions of the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) to explicitly include blockchains and smart contracts. As legal frameworks continue to evolve, the integration of smart contracts into mainstream business practices will become more prevalent, offering enhanced efficiency, security, and transparency.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are set to transform how we conduct transactions across various sectors by eliminating intermediaries and enhancing transparency and efficiency. As legal frameworks evolve to accommodate this technology, the integration of smart contracts into everyday business practices will continue to grow. For businesses looking to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving landscape, understanding and adopting smart contracts is essential.
For comprehensive blockchain solutions, contact Cogify today! We offer top-notch services with Swiss precision, ensuring your projects are secure, scalable, and future-proof.





