When it comes to design, most people tend to think about technical aspects such as layout, typography, and color schemes. However, the design goes beyond just aesthetics. It's about creating an experience that resonates with the user. And what better way to do that than by tapping into the power of emotions?
Emotions significantly impact how individuals interpret reality and motivate their actions. Positive experiences encourage growth, while negative experiences help prevent mistakes. Emotions associated with a product or service can affect user satisfaction and overall experience. Therefore, Emotional Design is crucial for a product or service's success.
In today's blog post, we'll explore the concept of Emotional design and how it can be used to enhance UX/UI, discussing best practices and insights for creating highly connected and memorable user experiences.
To fully understand emotional design, you first need to know the basics of UX/UI design.
Understanding Emotional Design
As users increasingly demand seamless and memorable digital experiences, emotional design has become an essential component of creating effective user interfaces.
Emotional Design is all about creating products that evoke emotional responses in users. When users feel emotionally attached to a product, they are more likely to engage with it, remember it, and recommend it to others. It requires understanding the psychology of emotions and using design elements such as color, typography, imagery, and content to create an emotional connection with the user. Emotional Design can be applied to any product, from physical products to digital interfaces.
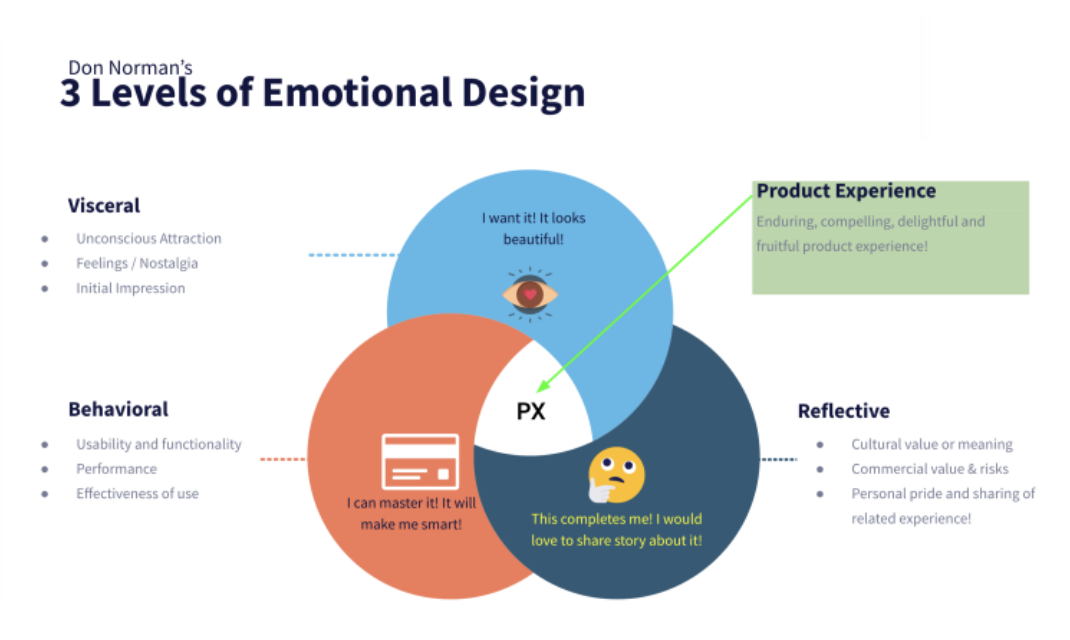
Don Norman, a user experience expert, presents theories that connect an individual's emotional state and their perception of design aesthetics, usability, and overall experience. A successful design should address three levels of processing - visceral, behavioral, and reflective - to create a holistic user experience that balances functionality with emotional resonance.
Emotional Design Components
-
Visceral design (appearance): focuses on the user's immediate emotional response or "first impressions" through aesthetics, colors, and images that draw their attention.
-
Behavioral design (usability): considers the usability and functionality of the product, influencing user behavior, with an uncluttered interface, simple navigation, and easy controls that make users feel in control.
-
Reflective design (personal impact): considers the deep message or purpose of the product in creating meaningful experiences for users after the interaction, shaping their overall impression of the design.
To form an emotional, lasting connection with their target audience, UX/UI designers must satisfy all three cognitive levels - visceral, behavioral, and reflective - as no single level is more important than the others.
The Impact of Emotional Design on User Experience
- Creates positive user engagement
- Builds loyalty and drives conversions
- Influences user behavior and decision-making
- Increases customer retention and reduces the bounce rate
- Taps into users' emotions and encourages exploration
- It can be measured by using user surveys, A/B testing, and user testing
- Measuring emotional impact is essential for the effectiveness of design
- Obtains valuable data about how users perceive products
Emotional design has a significant impact on user experience. It can make the difference between a product that is quickly forgotten and one that generates loyal followers. The impact of design elements on user emotions can be evaluated, allowing businesses to obtain valuable insights into user behavior and preferences, how emotionally attached they are to products, and whether or not emotional design strategies are effective.
Several companies have successfully implemented emotional design principles in their UX/UI.
Apple is known for creating products that evoke strong emotional connections with users. From the sleek design of its products to the carefully crafted interface, Apple creates a user experience that is both functional and emotionally satisfying.
Airbnb’s platform is designed to evoke emotions by showcasing beautiful images of unique homes, immersing users in a world of possibilities. Their website and mobile app create a sense of excitement and adventure while providing a seamless booking experience.
Google is also a great example of how emotional design can enhance user experience. Google’s search engine interface is clean, simple, and easy to use, evoking a sense of trust and reliability from users. Google’s focus on usability and functionality, combined with a visually pleasing design, has made it the most popular search engine today.
Best Practices for Incorporating Emotional Design
To create an engaging and personalized user experience, it is important to incorporate emotional design into your UX/UI. Here are some best practices to consider:

- Use microgestures to establish a connection with the user.
Incorporating microgestures, such as subtle animations or haptic feedback, into your UX/UI design can create a more personalized and engaging user experience. Additionally, using polite and light-hearted error messages can help alleviate user frustration and make negative experiences more tolerable.
- Use microcopy that is relatable to users
Effective microcopy can create a connection between users and your product or brand by utilizing a tone and voice that is relatable and consistent with the overall voice of your brand.
- Personalise the experience for each user
Personalization is a crucial component of emotional design as it gives users the impression that the product or service was tailored specifically to their needs. By showcasing content or products that align with the user's information and interests, you can make them feel valued and understood.
- Use storytelling to create an emotional connection
Using storytelling in your UX/UI design can establish an emotional connection between users and your product or brand by presenting it in a way that is relatable, engaging, and evokes positive emotions.
Incorporating small details into your UX/UI design can enhance the user experience and make it feel more polished and thoughtful, particularly in error messages where the use of polite and humorous language can help keep users engaged and offering incentives or rewards can help compensate for any inconvenience.
- Prioritize engagement and recognition
Focusing on engagement and recognition can help keep users interested and invested in your product or brand. Providing rewards or achievements for completing tasks or interacting with your product can motivate users to engage more with your website, improving their overall experience.
- Create a personal brand voice
Establishing a personal brand voice that aligns with your product or organization and includes a recognizable personality or mascot can enhance user identification. Your brand voice should be consistent with the tone and image of your product or organization to create a cohesive and memorable user experience, reflecting its personality and values.
- Use color and contrast to your advantage
Leveraging design elements like color, contrast, fonts, and multimedia can reinforce your brand's personality and set it apart from competitors. For example, using blue for banking instills trustworthiness. Incorporating video or sound can add depth to your brand and create an immersive experience that resonates with users.
Combining these best practices of emotional design into your UX/UI is a great way to create a more engaging user experience and develop a personal connection with users. Keep your audience's preferences and needs in mind to ensure the success of your website. Achieving a balance between simplicity and excitement will set your website apart from competitors.
Additionally, it's essential to remember to stay consistent with your brand voice and imagery, using design elements effectively to reinforce your brand's personality and values. This approach is vital to emotionally engaging with your target audience and building a long-lasting relationship with your users.

The Challenges of Emotional Design
Emotional design is a powerful tool, but it comes with its own unique set of challenges. One of the most significant obstacles is cultural differences. Given that different cultures have varying perceptions of color, symbols, and aesthetics, it's important to conduct thorough research on your target audience before implementing any design elements. By doing so, you can ensure that your design will resonate with your audience and avoid any potential misinterpretations.
Another challenge of emotional design is the risk of overdoing it. While incorporating emotional elements such as animations, videos, and interactive features can enhance UX, excessive use can lead to cluttered designs. To avoid overwhelming visitors with too much stimulation, it's essential to keep design elements simple, sparingly used, and purposeful. Always consider the primary goals of your website or product and prioritize functionality over aesthetics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Emotional Design is a powerful tool that enables designers to create products that resonate with users on an emotional level. By utilizing design elements that tap into the psychology of emotions, designers can create meaningful experiences that foster long-term engagement and loyalty. When it comes to UX/UI design, Emotional Design should be considered an essential component in the design process. So as designers, let's embrace Emotional Design and create products that inspire, excite, and delight users.





