Cybersecurity has become a critical concern for organisations of all sizes. Traditional security approaches, which rely on securing the network perimeter, are proving insufficient in today's environment. This is where Zero Trust Security comes in, offering a revolutionary approach to safeguarding digital assets by assuming that threats can come from both outside and inside the network.
Let’s dive deeper into this revolutionising way to protect digital assets.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity model that operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Unlike traditional security models that focus on protecting the perimeter of a network, Zero Trust assumes that threats can exist both outside and inside the network. Therefore, it requires continuous authentication and authorisation for every user, device, and application attempting to access resources.
The concept of Zero Trust was first introduced by John Kindervag, a former Forrester Research analyst, in 2010. His pioneering work laid the foundation for a security strategy that prioritises identity verification and strict access controls over assuming implicit trust within the network perimeter.
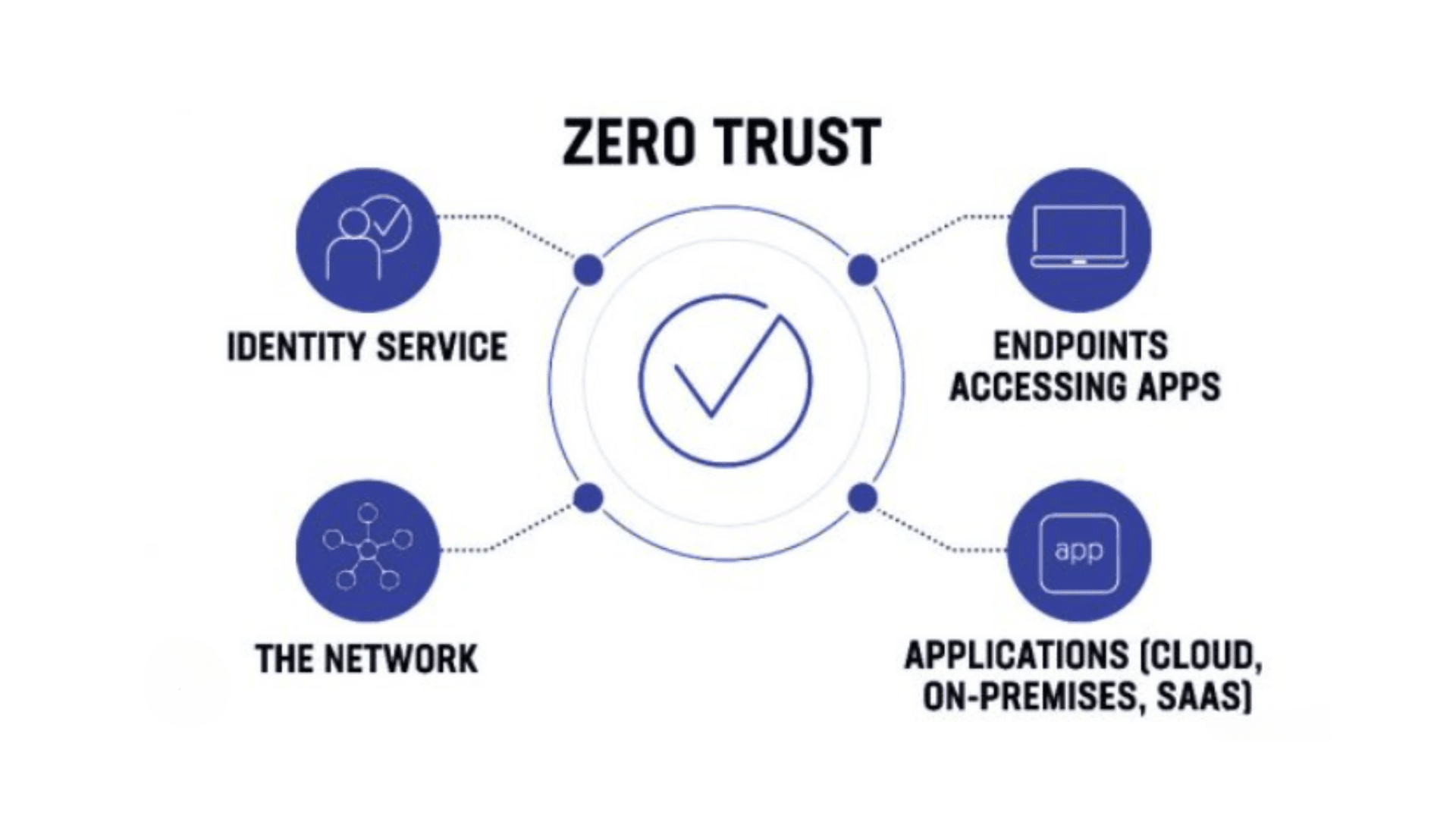
The Core Principles of Zero Trust Security
There are 3 core principles of Zero Trust Security:
1. Verify Explicitly
Zero Trust mandates that access to resources must be granted based on clear and precise verification. This means using a combination of data points such as user identity, location, device health, and more.
For example, implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) ensures that users provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorised access.
Also, Contextual Access Policies adapt based on the user's context, such as the time of access, the device being used, or the specific resource requested.
2. Least Privilege Access
This principle dictates that users and devices should only be granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks. By limiting access rights, organisations can reduce the attack surface and mitigate potential damage from compromised accounts.
For example, assigning Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) permissions based on roles within the organisation ensures that employees have only the access they need.
Additionally, granting Just-In-Time (JIT) temporary access to resources for a limited time period helps to minimise the window of opportunity for attackers.
3. Assume Breach
Zero Trust operates under the assumption that a breach has either already occurred or is inevitable. This mindset shifts the focus to detecting and responding to threats quickly, rather than solely relying on preventative measures, by implementing advanced monitoring tools to detect unusual activity in real time.
Zero trust also includes preparing Incident Response Plans for preparedness measures that enable quick isolation and remediation of compromised segments of the network.
The Benefits of the Zero Trust Security
Cyber threats are continuously evolving, with attackers employing sophisticated techniques to bypass traditional defences. Zero Trust Security provides a dynamic and adaptable framework to counteract these advanced threats.
Additionally, the modern IT landscape is characterised by a mix of on-premises and cloud-based resources, remote workforces, and IoT devices. Zero Trust's granular approach to security makes it well-suited for managing these complex environments.
There are several benefits of adopting a Zero Trust approach, including:
- Enhanced Security Posture: By continuously verifying access requests and limiting privileges, Zero Trust significantly reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Zero Trust principles align with many regulatory requirements, helping organisations maintain compliance.
- Operational Efficiency: Automated verification processes and streamlined access controls can lead to improved operational efficiency.

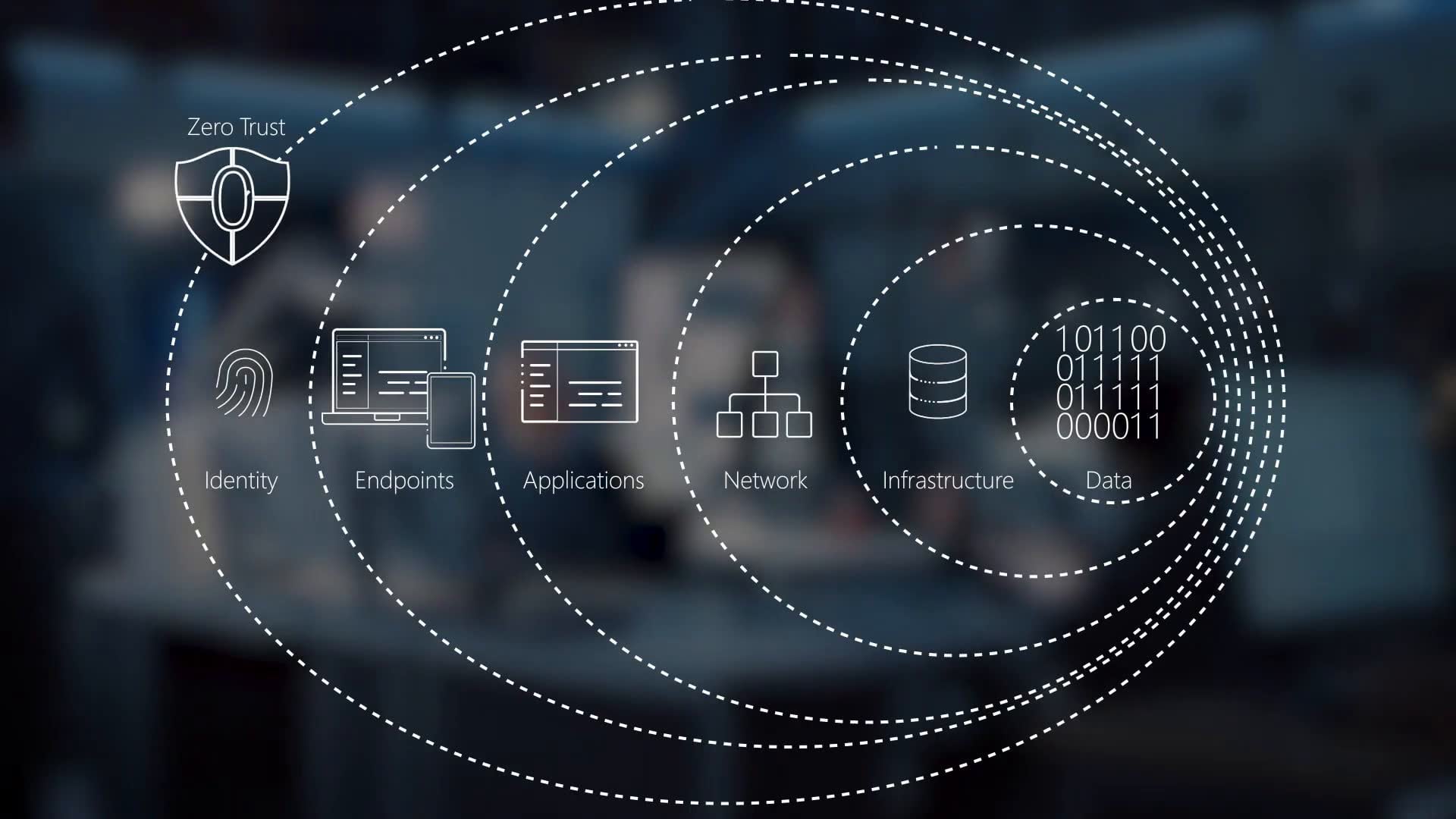
The 5 Pillars of Zero Trust Security
There are 5 pillars of a Zero Trust Security that work together to create a secure and effective security model, including:
1. Identity Verification
Ensuring that only authenticated and authorised identities gain access is fundamental to Zero Trust Security. Strong authentication methods, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), are crucial.
MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors, making it harder for attackers to gain access using stolen credentials. Utilising robust authentication mechanisms, including biometrics and hardware tokens, further enhances user identity validation.
2. Device Security
Maintaining a secure device environment is critical to preventing unauthorised access. Ensuring that devices comply with security policies involves regular updates and patches to address vulnerabilities.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools are essential for monitoring and managing device security, ensuring that only secure and compliant devices can access the network. Deploying EDR solutions helps protect endpoints against threats and maintains a strong security posture.
3. Network Segmentation
Dividing the network into smaller, more manageable segments limits the scope of potential breaches. Micro-segmentation involves creating isolated segments within the network, each with its own security controls.
This approach minimises lateral movement by attackers, making it harder for them to spread once they breach the perimeter. Implementing strict access controls between segments helps contain threats and prevent their spread across the network.
4. Application Security
Safeguarding applications and workloads is crucial for maintaining overall security. This involves implementing security measures such as secure coding practices, application firewalls, and regular vulnerability assessments.
Adopting best practices in application development and deploying web application firewalls (WAF) protects applications from attacks. Regular security testing helps detect and fix vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, ensuring the integrity of applications and workloads.
5. Data Protection
Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data is paramount in Zero Trust Security. Encryption and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies are essential to protect sensitive information.
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit ensures that it remains confidential and intact. Implementing DLP measures helps prevent data breaches and unauthorised access. Adhering to data protection regulations and maintaining high standards for data processing and storage ensure data privacy and integrity.
Is Zero Trust Security Right for Your Organisation?
You are probably wondering if this security model is the right fit for your organisation.
Well, as cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting a Zero Trust Security framework is becoming essential for future-proofing your organisation. This approach not only protects digital assets but also prepares you for emerging challenges by continuously validating each access request.
To determine if Zero Trust is right for your organisation: assess your current cybersecurity posture, identify gaps in access control, and evaluate the sensitivity of your data.
Organisations handling critical or confidential information, or those subject to regulatory compliance, will particularly benefit from Zero Trust.
Contact us at Cogify today to learn how we can tailor a robust security solution for your organisation and ensure your digital assets are protected against modern threats.





